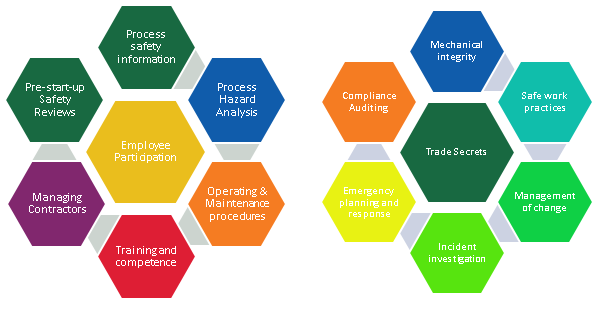
Industries that handle hazardous materials, such as chemical plants, oil refineries, and manufacturing facilities, face significant safety risks. The complexity and potential danger inherent in these environments demand a structured approach to safety management. This is where Process Safety Management (PSM) plays a pivotal role in safeguarding not only the workers but also the surrounding environment. Implemented effectively, PSM minimizes risks associated with hazardous processes and reduces the likelihood of catastrophic incidents.
Understanding Process Safety Management (PSM)
At its core, Process Safety Management is a comprehensive framework designed to prevent accidents involving the release of hazardous chemicals or energy. PSM is not just about compliance but about fostering a safety culture that prioritizes the identification, assessment, and mitigation of risks.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) established specific PSM regulations to ensure that high-hazard industries adhere to rigorous safety standards. PSM involves detailed documentation, risk analysis, and continuous monitoring to address potential failures in equipment, procedures, or human actions that could lead to significant hazards.
Risk Identification and Hazard Analysis
One of the most important aspects of PSM is identifying and analyzing hazards within high-risk operations. Industries that deal with explosive or toxic substances are inherently dangerous, and the first step toward minimizing these dangers is understanding where they come from.
Process hazard analysis (PHA), a key component of PSM, is a systematic approach that helps identify the potential risks in processes involving hazardous chemicals. Through methodologies like Hazard and Operability Study (HAZOP) or Fault Tree Analysis (FTA), companies can gain a detailed understanding of vulnerabilities in their operations. This proactive identification of risks is critical in high-hazard industries where even a minor oversight can lead to major incidents.
Equipment Integrity and Preventive Maintenance
Equipment failure is one of the leading causes of accidents in high-hazard industries. Ensuring the mechanical integrity of critical equipment—such as reactors, storage tanks, and piping systems—is fundamental to minimizing risks. Under PSM, strict maintenance procedures are enforced, and equipment must undergo regular inspections to ensure it operates safely.
Preventive maintenance strategies, as mandated by PSM, go beyond routine checks. They include predictive analytics and the use of advanced technology to anticipate potential failures before they occur. This approach is particularly important in industries handling flammable or toxic substances, where equipment failure can lead to catastrophic events.
Employee Training and Competence
Human error is another significant risk factor in high-hazard environments. Inadequate training or a lack of knowledge about specific procedures can lead to accidents. PSM addresses this issue by requiring that all employees involved in hazardous processes receive thorough training.
Employees must be educated not only on operational procedures but also on how to identify potential hazards and respond to emergencies. Furthermore, PSM mandates regular refresher training to ensure employees remain competent and informed about the latest safety protocols. A well-trained workforce is essential to preventing incidents caused by human error, and this continuous focus on education and competency development is critical in industries where the stakes are high.
Emergency Response and Incident Management
Despite the best preventive efforts, emergencies can still occur. PSM helps minimize the impact of such events by ensuring companies have robust emergency response plans in place. These plans include clear guidelines on how to respond to fires, chemical releases, or explosions, ensuring that employees know exactly what to do in the event of an emergency.
Additionally, PSM requires thorough incident investigation procedures. If an incident does occur, companies must analyze the root cause, identify the factors that contributed to it, and implement corrective actions to prevent similar events from happening in the future. This constant learning cycle helps build a more resilient safety culture over time.
Continuous Improvement and Compliance
High-hazard industries are constantly evolving due to technological advancements and regulatory updates. PSM emphasizes the need for continuous improvement in safety practices, requiring companies to regularly review and update their safety management systems. By staying compliant with regulations and adapting to new standards, businesses can ensure that their safety protocols remain effective and relevant.
PSM also promotes a culture of accountability and transparency. Regular audits are conducted to assess whether safety practices are being followed, and any gaps are immediately addressed. This ongoing monitoring and evaluation process is vital in industries where a single lapse in safety can have severe consequences.
The Role of Safety Culture in High-Hazard Industries
While PSM provides a structured approach to managing safety risks, the true effectiveness of this system relies heavily on the overall safety culture within an organization. A strong safety culture encourages employees to prioritize safety, report hazards, and take proactive steps to mitigate risks.
In high-hazard industries, where the margin for error is incredibly thin, fostering such a culture is essential. Leaders must promote open communication about safety concerns and actively involve workers in the decision-making process related to safety protocols. When employees feel empowered to contribute to safety initiatives, the organization as a whole benefits from a safer and more resilient working environment.
Conclusion
Process Safety Management is an essential tool in minimizing risks in high-hazard industries. By focusing on hazard identification, equipment integrity, employee competence, and emergency preparedness, PSM ensures that companies are well-equipped to prevent accidents and respond effectively when they occur. As industries continue to evolve and new hazards emerge, the role of PSM in maintaining safety and operational excellence will remain critical. Through continuous improvement, regular compliance, and a strong safety culture, high-hazard industries can significantly reduce risks and protect both their employees and the environment.